Windows Server Datacenter: Azure Edition – L’evoluzione cloud-first di Windows Server
Nel novembre 2024 Microsoft ha rilasciato Windows Server 2025 e, contestualmente, ha aggiornato la sua variante “cloud-only”: Windows Server Datacenter: Azure Edition. Pur condividendo lo stesso codice base del nuovo sistema operativo, l’edizione Azure è ottimizzata esclusivamente per l’esecuzione all’interno delle macchine virtuali di Microsoft Azure (e delle loro repliche on-prem tramite Azure Local, prima conosciuto come Azure Stack HCI). In questo articolo analizziamo quali funzionalità la distinguono oggi e perché potrebbe essere la scelta migliore per chi gestisce workload critici nel cloud.
Aggiornamenti più rapidi e senza riavvio
-
Hotpatching GA
- In Azure Edition gli aggiornamenti di sicurezza vengono applicati “a caldo”, senza riavvio né interruzione del servizio. Ne ho parlato nell’articolo Hotpatch per Windows Server 2022 Azure Edition con Desktop Experience – ICT Power
- Sulle edizioni Standard e Datacenter lo stesso meccanismo è disponibile solo se il server è connesso ad Azure Arc, con qualche limitazione (ad es. finestre di manutenzione più ristrette). Ne ho parlato nell’articolo Abilitare la funzionalità di Hotpatch (preview) in Windows Server 2025 – ICT Power
- Rilascio continuo delle feature
L’edizione Azure riceve nuove funzionalità ogni anno tramite Windows Update, mentre le altre edizioni le ottengono solo nei rilasci “major” successivi
Integrazione “zero-touch” con la piattaforma Azure
- Azure Automanage applica automaticamente best practice, backup, monitoring e baseline di sicurezza. Ne ho parlato nell’articolo Disponibili Windows Server 2022: Azure Edition (general availability), hotpatch (preview), automanage (preview) e configuration management (preview) in Microsoft Azure – ICT Power
- Azure Update Manager e Microsoft Defender for Cloud sono abilitati senza costi aggiuntivi di licenza (si paga il consumo della VM). Ne ho parlato nell’articolo Gestire gli aggiornamenti dei server ibridi di Azure Arc con Azure Update Manager – ICT Power
- Licensing semplificato: niente KMS o MAK; l’attivazione è gestita dal fabric di Azure
Sicurezza e compliance by design
- Integrato con Microsoft Entra ID per l’accesso just-in-time alle VM.
- VBS (Virtualization-Based Security) e Secure Boot abilitati di default nelle immagini di marketplace.
- Defender for Cloud abilita la raccomandazione di hardening automatica e l’analisi delle vulnerabilità sui pacchetti applicativi.
Rete e storage ottimizzati per il cloud
- Azure Extended Networking: consente di spostare o migrare VM mantenendo gli stessi indirizzi IP, utile in scenari di disaster-recovery o di migrazione graduale. Ne ho parlato nell’articolo Configurare Azure Extended Network per permettere le estensioni L2 delle reti on-premises – ICT Power
- SMB over QUIC: condivisione file sicura (TLS 1.3) che usa il protocollo QUIC invece di TCP, eliminando la necessità di VPN tradizionali per l’accesso remoto. Ne ho parlato nell’articolo Windows Server 2025 – Implementare SMB over QUIC – ICT Power
Differenze chiave rispetto a Standard/Datacenter
- Ambiente di esecuzione: Azure Edition vive solo in Azure o in guest VM su Azure Local; le altre edizioni supportano anche l’hardware on-premises.
- Hotpatching: nativo in Azure Edition; su Standard/Datacenter è disponibile solo in preview e richiede Azure Arc.
- Funzionalità di rete avanzate: Extended Networking è esclusivo di Azure Edition; su altre edizioni si ricorre a soluzioni di terze parti o a redesign della subnet.
- Cadenza degli aggiornamenti: Azure Edition riceve feature update annuali; Standard/Datacenter solo con nuove versioni LTSC.
- Licensing: costi inclusi nel consumo della VM; sulle edizioni tradizionali serve acquisto di licenze o Software Assurance.
Trovate maggiori informazioni nell’articolo Confronto tra le edizioni Standard, Datacenter e Datacenter: Azure Edition di Windows Server 2022 – ICT Power e sulla pagina ufficiale Comparison of Windows Server editions | Microsoft Learn
| Feature | Subfeature | Standard edition | Datacenter edition | Datacenter: Azure Edition |
| .NET Framework 3.5 Features | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| .NET Framework 4.8 Features | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Activation | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Automatic Virtual Machine Activation | ⚠️ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Key Management Service (KMS) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | |
| Active Directory Certificate Services | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Certificate Enrollment Policy Web Service | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Certificate Enrollment Web Service | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Certification Authority | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Certification Authority Web Enrollment | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Network Device Enrollment Service | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Online Responder | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Active Directory Domain Services | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Active Directory Federation Services | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Active Directory Rights Management Services | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Azure Extended Networking | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | |
| Background Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| BitLocker Drive Encryption | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| BitLocker Network Unlock | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| BranchCache | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Client for NFS | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Data Center Bridging | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Device Health Attestation | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| DHCP Server | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Direct Play | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| DLNA codecs and web media streaming | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| DNS Server | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Enhanced Storage | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Failover Clustering | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Fax Server | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| File and Storage Services | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| BranchCache for Network Files | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Data Deduplication | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| DFS Namespaces | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| DFS Replication | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| File Server | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| File Server Resource Manager | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| File Server VSS Agent Service | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| iSCSI Target Server | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| iSCSI Target Storage Provider (VDS and VSS hardware providers) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Server for NFS | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| SMB 1.0/CIFS File Sharing Support | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| SMB Bandwidth Limit | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| SMB over QUIC | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Work Folders | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Storage Migration Service | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Storage Migration Service Proxy | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Storage Spaces | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Storage Spaces Direct | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Storage Replica | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Group Policy Management | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Host Guardian Hyper-V Support | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Host Guardian Service | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Hotpatching | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| I/O Quality of Service | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| IIS Hostable Web Core | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| IP Address Management (IPAM) Server | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Management OData IIS Extension | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Media Foundation | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Message Queuing | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Message Queuing DCOM Proxy | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Message Queuing Services | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Microsoft Defender Antivirus | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Multipath I/O | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| MultiPoint Connector | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Network ATC | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Network Controller | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Network Load Balancing | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Network Policy and Access Services | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Network Virtualization | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Print and Document Services | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Internet Printing | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Line Printer Daemon (LPD) Service | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Print Server | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Quality Windows Audio Video Experience | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| RAS Connection Manager Administration Kit (CMAK) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Remote Access | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| DirectAccess and VPN (RAS) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Routing | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Web Application Proxy | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Remote Assistance | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Remote Desktop Services | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Remote Differential Compression | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Remote Server Administration Tools | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| RPC over HTTP Proxy | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Setup and Boot Event Collection | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Simple TCP/IP Services | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| SNMP Service | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Software Load Balancer | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| System Data Archiver | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| System Insights | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Telnet Client | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| TFTP Client | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Virtualization | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Containers | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | |
| Hyper-V | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| GPU partitioning | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| VM Shielding Tools for Fabric Management | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Volume Activation Services | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Web Server (IIS) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| FTP Server | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Web Server | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| WebDAV Redirector | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Windows Biometric Framework | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Windows Deployment Services | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Windows Identity Foundation 3.5 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Windows Internal Database | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Windows PowerShell | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Windows PowerShell 2.0 Engine | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Windows PowerShell 5.1 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Windows PowerShell Desired State Configuration Service | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Windows PowerShell Web Access | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Windows Process Activation Service | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Windows Server Management enabled by Azure Arc | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Azure Update Manager | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Change Tracking and Inventory | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Azure Machine Configuration | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Windows Admin Center in Azure for Arc | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Remote Support | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Network HUD | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Best Practices Assessment | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Azure Site Recovery Configuration | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Windows Search Service | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Windows Server Backup | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Windows Server Migration Tools | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Windows Server Update Services | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Windows Standards-Based Storage Management | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Windows Subsystem for Linux | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Windows TIFF IFilter | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| WinRM IIS Extension | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| WINS Server | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Wireless LAN Service | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| WoW64 Support | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| XPS Viewer | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
Per creare una nuova VM con Windows Server 2022 oppure Windows Server 2025 Azure Edition potete collegarvi al link Microsoft Azure Marketplace oppure scegliere l’immagine da utilizzare direttamente al momento della creazione della Azure VM.
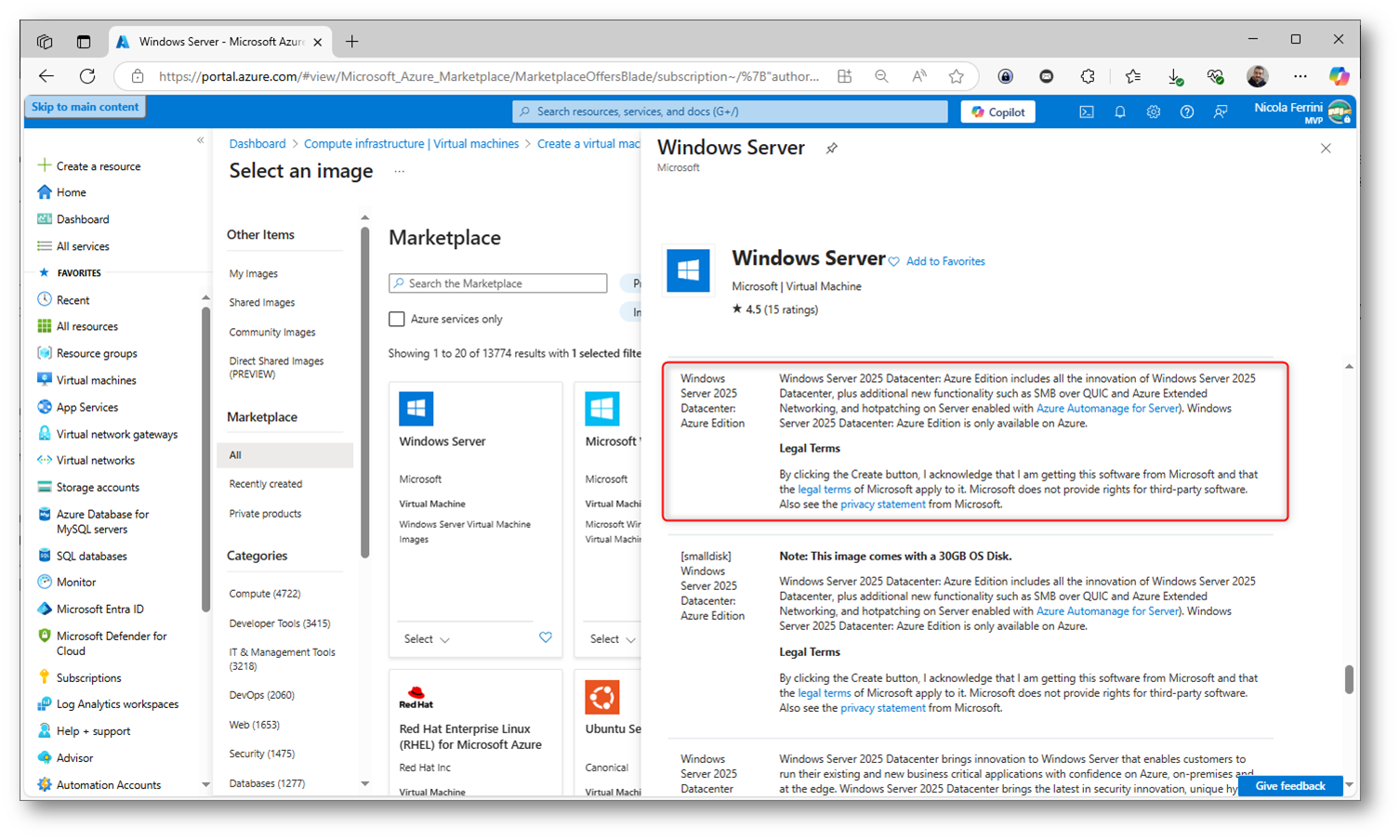
Figura 1: Immagine di Windows Server 2025: Azure Edition presente nel marketplace di Microsoft Azure
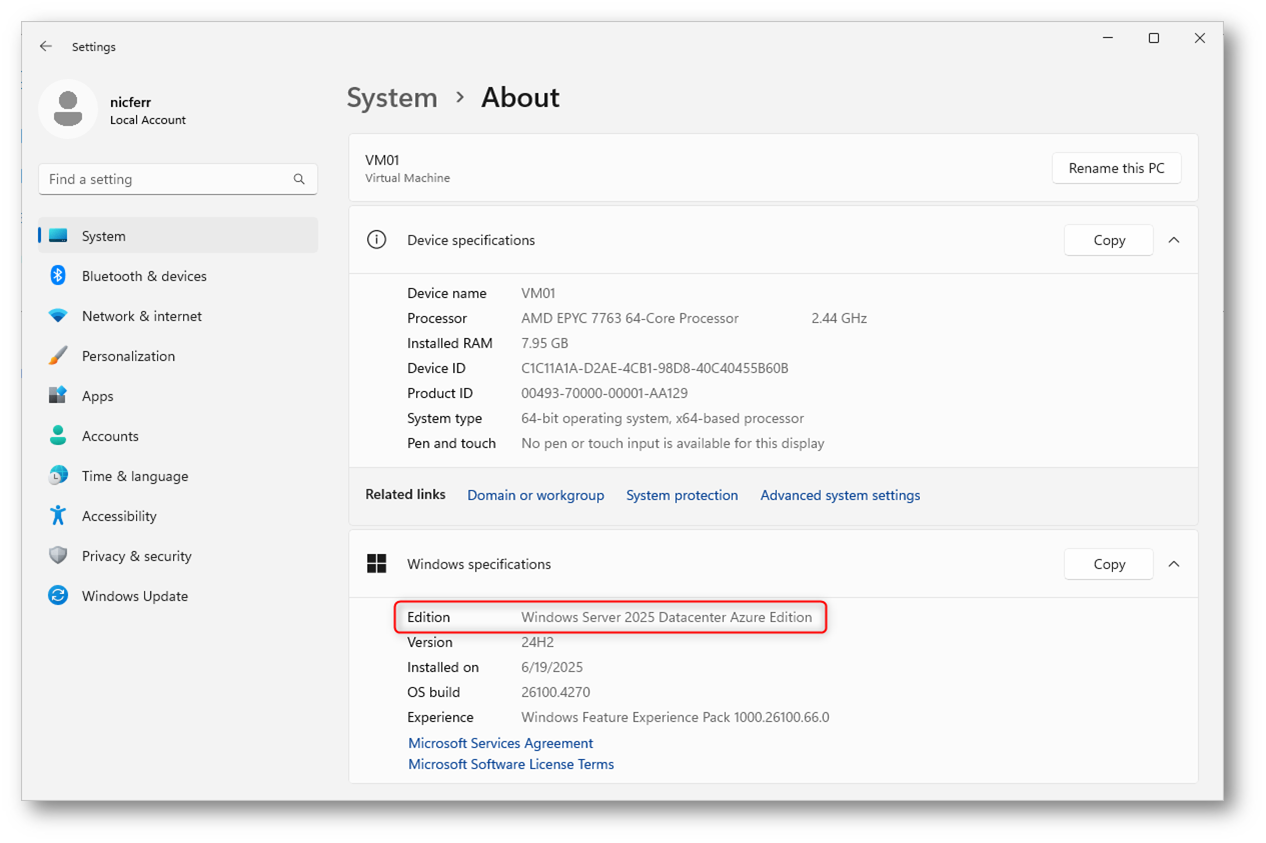
Figura 2: Windows Server 2025 Datacenter Azure Edition
Quando scegliere Azure Edition
- Workload mission-critical 24×7: database, ERP, applicazioni che non possono permettersi downtime per patch.
- Migrazioni lift-and-shift che richiedono di mantenere gli stessi IP (con Extended Networking) o file share sicure via Internet (con SMB over QUIC).
- Progetti DevOps e IaC che puntano su automazione completa: Azure Automanage riduce la configurazione manuale.
- Disaster recovery in Azure: replica di VM on-prem su Azure con failover rapido e senza riconfigurare l’indirizzo IP del servizio.
Limitazioni da conoscere
- Non può essere installata su server fisici o hypervisor di terze parti.
- I container Windows sono supportati, ma per scenari Kubernetes conviene usare AKS o Windows Server Standard/Datacenter in cluster.
- Alcune funzioni (es. hotpatch on-prem) richiedono servizi a pagamento o licenza aggiuntiva fuori da Azure.
Conclusioni
Se la vostra strategia IT punta a sfruttare l’elasticità di Azure per applicazioni che devono restare sempre operative, Windows Server Datacenter: Azure Edition offre oggi (2025) il mix più completo di availability, gestione automatizzata e sicurezza di default. Riduce il lavoro manuale, minimizza i downtime da patching e integra nativamente tutte le best practice di Microsoft per il cloud ibrido.

